Anatomy of the Human Heart
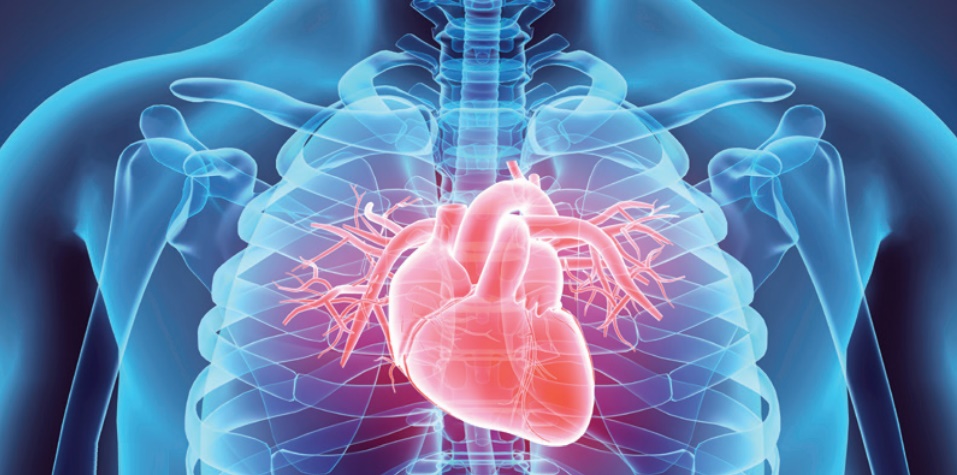
The human heart is roughly the size of a closed fist and is located in the thoracic cavity, between the lungs, slightly to the left of the sternum (breastbone). It is protected by the ribcage and rests on the diaphragm, a muscular partition separating the chest and abdomen. The heart is composed of specialized cardiac muscle tissue, known as myocardium, which contracts rhythmically to pump blood.
Function of the Human Heart
The primary function of the human heart is to pump blood throughout the body, ensuring the delivery of oxygen, nutrients, hormones, and other essential substances to various organs and tissues. It also helps remove waste products like carbon dioxide and metabolic byproducts. The heart accomplishes this through a coordinated contraction and relaxation process, commonly known as the cardiac cycle, which is controlled by electrical signals.
Location of the Human Heart
The human heart is positioned slightly to the left side of the chest, with about two-thirds of its mass located to the left of the midline. The apex, the pointed bottom of the heart, rests just above the diaphragm and points slightly towards the left side. However, it is important to note that the heart's location can vary slightly among individuals, especially those with specific medical conditions or anatomical variations.
Interesting Facts about the Human Heart
The heart beats approximately 100,000 times a day, pumping around 2,000 gallons (7,500 liters) of blood.
Contrary to popular belief, the heart does not look like the symmetrical heart shape often depicted; its actual shape is more like a cone.
The sinoatrial (SA) node, often referred to as the heart's natural pacemaker, initiates the electrical impulses that coordinate the heart's contractions.
The heart is the first organ to develop in the human fetus, and its rhythmic contractions usually begin around the 22nd day of gestation.
Physical exercise and a healthy lifestyle can strengthen the heart muscle and improve its efficiency.
Heart disease, including conditions like coronary artery disease and heart attacks, is one of the leading causes of death worldwide. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle and regular medical check-ups are crucial for heart health.
Conclusion
The human heart is a remarkable organ responsible for circulating blood throughout the body. Its four chambers work together to ensure the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to various organs and tissues. Understanding the anatomy, function, and location of the heart helps us appreciate its importance in sustaining life. By taking care of our hearts through a healthy lifestyle, we can contribute to our overall well-being and reduce the risk








0 Comments